How Much Weight Can a 2×4 Wall Hold? Helpful Expert Guide
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
How Much Weight Can a 2X4 Wall Hold?
Are you planning to install new shelves, hang cabinets, install a TV, or build additional storage in your garage? Knowing how much weight can a 2×4 wall hold is crucial.
Whether you’re working with a load-bearing wall or just partitioning rooms, knowing the weight capacity helps ensure that your project stays both safe and durable over time.
Here is the short answer:
You can hang up to 600 pounds on a 2X4 stud wall provided you distribute the load over 3 studs, use 12 #8 2-inch construction screws as fasteners, and keep the load close to the garage wall.
How much weight a 2×4 wall can hold depends on the type of wood, lumber grade, and wall configuration, as they all affect its strength.
Specifically, the following are some of the factors that determine the calculated 2X4 wall load-bearing capacity of the garage wall framed with wood studs:
- The width of the wall which determines the number of studs (usually spaced 16″ OC)
- Stud dimension (usually 2X4, though sometimes 2X6 may be used)
- Height of the stud (a standard garage has an 8′ high wall)
- Type of wood used (spruce, pine, fir are commonly used)
- Type of fastener (construction screws can hold more than nails)
- Stud dampness level

When an item is hung on a garage wall it creates a shear load on the fastener (nail or screw). The shear load is the weight of the object being pulled down by gravity and trying to produce a sliding failure in the fastener.
The load also tries to pull the fastener out of the stud like a hammer claw. This is the “pull out” load or the “withdrawal” load.
In addition, the load of the item is also trying to twist the stud along its vertical height. This is the torque on the stud which can warp or bow the stud.
That’s why it’s important to work within the limits provided by building codes and span tables—especially for DIYers looking to maximize vertical storage space.
Basics of a 2×4 Stud Wall
Before diving into specific weight limits and load-bearing capacity, it’s helpful to understand the role 2×4 walls play in home construction.
Knowing whether you are working with a load-bearing or non-load-bearing wall is key since these two types of walls have vastly different weight capacities.
What is a 2×4?
Despite being called a “2×4,” the actual dimensions of 2×4 studs are 1.5 inches by 3.5 inches. 2x4s are the most common choice for framing walls in homes, garages, and sheds.
Their popularity is due to their versatility, availability, and affordability. They are essential for building:
- Interior walls (both load-bearing and partitioning walls)
- Garage walls, often used to mount cabinets and shelving
- Exterior walls (though thicker lumber, like 2x6s, is sometimes preferred for better insulation)
Load-Bearing vs. Non-Load-Bearing Walls
A critical distinction when planning to hang or mount anything on a 2×4 wall is whether the wall is load-bearing or non-load-bearing.
- Load-bearing walls:
- These walls carry the weight of the structure above them, such as the roof, floors, or an additional story.
- Weight Limit Example: A properly built load-bearing 2×4 wall can support thousands of pounds distributed vertically.
- Non-load-bearing walls:
- These walls only act as room dividers and don’t support structural weight.
- They still offer some weight capacity for light shelves or decor, but mounting heavy items directly onto these walls can lead to sagging or even collapse.
Expert Tip: “Always check if your wall is load-bearing before making modifications. Knocking down or adding weight to a load-bearing wall without reinforcement can be a structural disaster.”
Factors That Affect the Weight Capacity of a 2×4 Wall
The weight capacity of a 2×4 wall is not a fixed number—it depends on several factors that influence the wall’s overall strength. Here are some of the key factors explained.
1. Wood Species and Grade of Lumber
The type of wood used in the 2×4 stud is central to its load-bearing capacity. Common framing woods like pine, spruce, and Douglas fir, (SPF) are known for their balance of strength and affordability.
However, hardwoods and high-grade lumber can support more weight.
- Lumber Grades: No. 1 and No. 2 are the most frequently used for wall framing. No. 1 grade lumber offers superior strength and weight capacity, while No. 2 is slightly weaker but more cost-effective.
Expert Tip: “For heavy-duty projects like garage cabinets, opt for higher-grade lumber to improve the wall’s durability.”
2. Stud Spacing and Wall Design
The spacing between 2×4 studs determines the garage wall’s load-bearing capacity. Standard practice is 16 inches on center, though some non-load-bearing walls may use 24 inches between studs.
- Closer Stud Spacing = Stronger Wall: Reducing spacing improves the wall’s ability to support more weight.
- Using Span Tables: Span tables provide detailed guidelines for weight limits based on stud spacing and wall height. These tables help ensure that your wall complies with building codes.
3. Modulus of Elasticity and Extreme Fiber Stress (Fb Value)
These technical terms measure the strength and flexibility of wood under stress. For homeowners, these values offer insight into whether the wood will bend or break under a heavy load.
- Modulus of Elasticity (E value): Measures how much a piece of lumber will deform under stress. Higher E values indicate stronger wood that resists bending.
- Extreme Fiber Stress in Bending (Fb value): This represents the weight the wood can bear before breaking. The higher the Fb value, the higher the weight capacity.
4. Environmental Factors
Temperature and moisture levels also affect wood strength. High moisture content will compromise the garage wall’s load-bearing capacity.
Proper ventilation in garages is important for maintaining the wood’s integrity.

Typical Weight Limits for 2×4 Walls
The weight limit of a 2×4 wall depends on whether the wall is load-bearing or non-load-bearing, how the weight is applied (vertical or horizontal), and whether proper installation practices are followed.
Is the 2×4 Wall Load Bearing Capacity Same in Every Direction?
The 2×4 wall load-bearing capacity is not the same in every direction. It is strongest when the load is applied perpendicular to the wood grain.
- A 2×4 stud can hold more weight when standing upright than when laid on its side.
- Wood is stronger in tension than compression.
- A 2×4 stud weakens with length, as longer studs are more prone to buckling under load.
Here are some common weight scenarios to help you better understand what your 2×4 wall can safely support.
Non-Load-Bearing Walls
- Weight Capacity: Roughly 15 to 20 pounds per linear foot.
- Use Case: Non-load-bearing (typically partition walls) walls are OK for mounting lightweight items like framed pictures or shelves for keeping lightweight items such as books or sportswear.
Expert Tip: “Try not to hang anything directly onto the drywall. Always attach the item to the studs.”
Load-Bearing Walls
The load capacity of a 2×4 wood stud depends on the direction of the load.
How Much Weight Can a 2×4 Stud Support Vertically?
Each 2X4 wood stud used for framing garage walls can support around 1000 pounds vertically. Please note that this is the compressive load.
In theory, a 24’X24′ garage with 80 wood 2×4 wall studs could support a roof weighing 80,000 pounds.
The vertical or compressive load is passed through the wall studs onto the garage foundation.
Expert Tip: “However, torque can cause the studs to bow and ultimately snap, much before the compressive load limit is reached.”
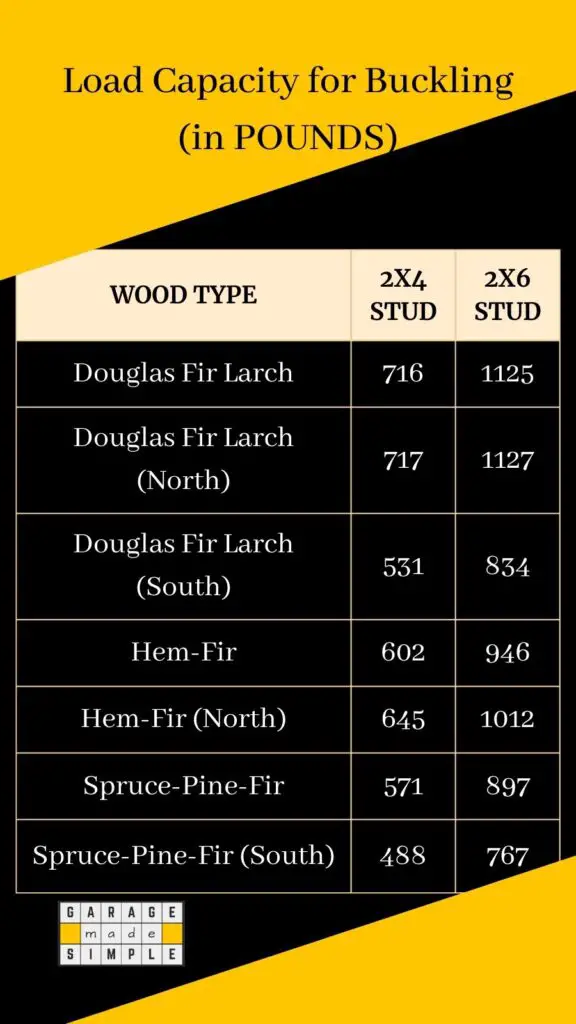
A vertical 8′ high 2X4 stud will buckle at loads ranging from 488 – 717 pounds. So a garage wall framed using 20 2X4 wood studs can support a roof load of 10,000 – 15,000 pounds, without buckling.
The capacity of a wood stud is the constant load that will cause it to buckle. You can calculate this using the “capacity of wood column calculator” by Jonathan Ochshorn.
A sample calculation for different wood types is given below:
How Much Weight Can a 2×4 Stud Support Horizontally?
A 2X4 wood stud can support 20 – 40 pounds per linear foot of horizontally applied loads. So each 2X4 wood stud in an 8’ wall can support 160 – 320 pounds of weight hung on it.
The calculation depends on several factors including the type of wood. Anyway, this factor is relevant when calculating loads hung from the garage ceiling.
When hanging loads such as cabinets or shelves from garage wall studs, concentrating too much weight in one spot, even on a load-bearing wall, can cause studs to bow or drywall to crack. So ensure even distribution.
In any case, the role of the fasteners (nails or screws) takes precedence over the load capacity of the 2×4 wall stud.
How Much Weight Can a Nail in a Stud Hold?
There are quite a few nail types available at a hardware store. The one that you are likely to use for hanging something on your garage wall is going to be a common nail.
A common nail can hold about 20 pounds.
Common nails are fine for hanging light loads, such as a picture frame, to a stud. Try using nails with rings or twists in them. It increases the gripping strength. Choose a longer nail such as 10d (3”) or 16d (3 ½”), as they will be harder to get pulled out by the torque of the weight.
For heavier loads such as racks or cabinets, nails are not practical. You must use screws as they can grip the wood stud.
How Much Weight Can a Screw Hold in a Stud?
A good quality construction screw can hold 80 – 100 pounds.
The most effective way of using screws for hanging racks, cabinets, etc. is to use a large number of screws and spread out the load.
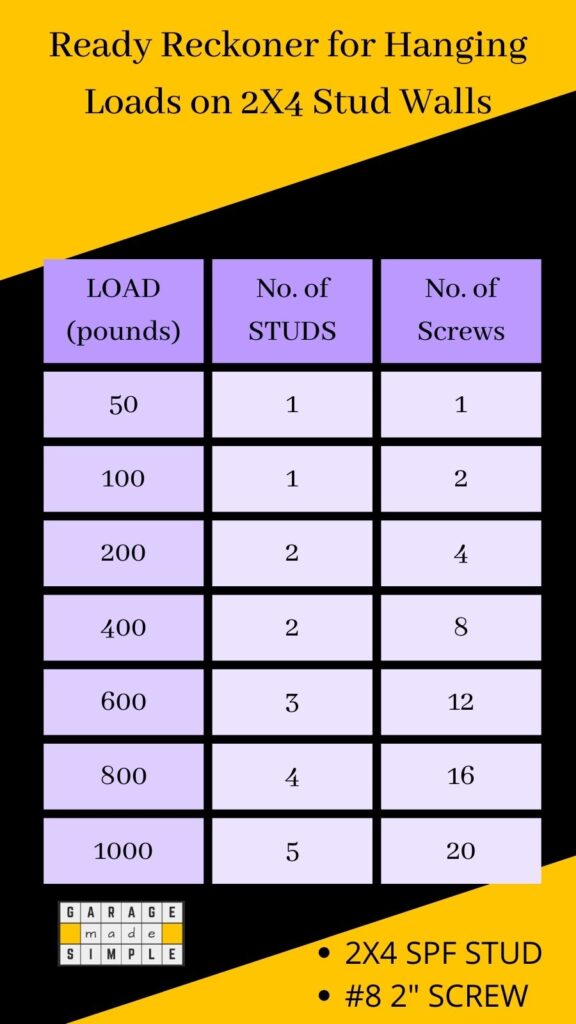
For example, if you are hanging a cabinet which will weigh 600 pounds, spread the weight over three studs using 9 – 12 screws. That way the load on each stud is 200 pounds and the load on each screw is 50 – 67 pounds.
You could use #8 2” screws to give the strength & the grip required. I recommend keeping VIGRUE #6#8#10 Black Wood Screws Assortment Kit in your stock.
How to Calculate the Number of Studs & Screws to Use?
The safe limits on how much weight can a 2X4 stud wall hold:
- The distributed load per stud should not exceed load capacity for buckling based on the wood type of the stud. To be on the safe side keep it at 50% or less
- The distributed load per screw should not exceed 50% of the allowable withdrawal load.
Let us say you need to hang a cabinet that will weigh 600 pounds.
- Distribute the load on three SPF (spruce-pine-fir) studs. The load per stud would be 200 pounds which is less than 50% of the load capacity for buckling of a 2X4 SPF stud (488 pounds).
- Use a total of 12, #8 screws (4 per stud) evenly distributed. The load per screw will be 50 pounds. This is slightly over 50% of the allowable withdrawal load per screw if the penetration is 1”.
- It is OK, but play it safe and use a screw that has a penetration of 1 ½” or even 2”.
Quick Calculation & Ready Reckoner
As a quick but safe calculation of how much weight can a 2X4 stud wall hold, use these quick formulas:
No. of Studs = Load divided by 200 and rounded up
No. of Screws = Load divided by 50 and rounded up for even spacing
Best Practices for Safely Adding Weight to 2×4 Walls
You can maximize the weight capacity of your 2×4 wall while ensuring safety. The trick is in proper installation techniques and reinforcement methods.
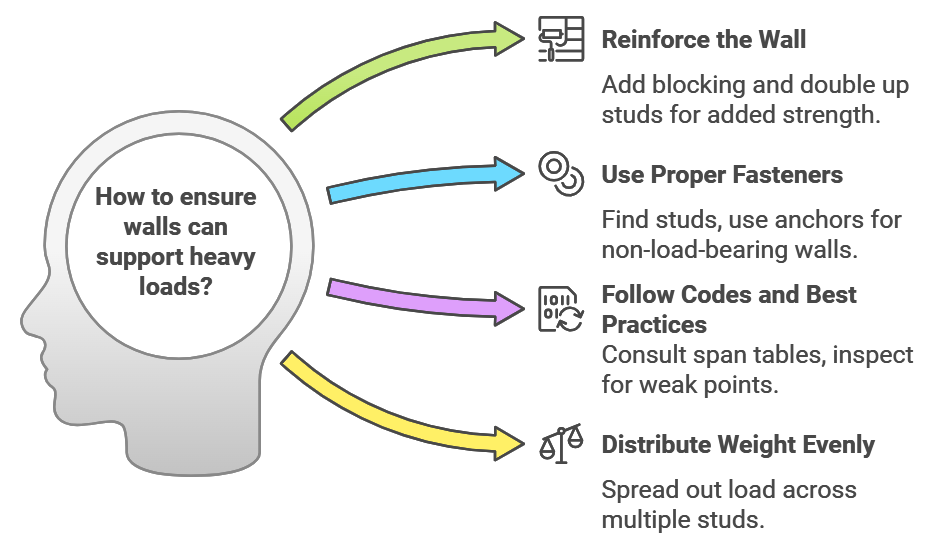
Whether you’re mounting heavy cabinets, gym equipment, or shelves, following these best practices will help you avoid structural issues.
1. Reinforce the Wall for Heavier Loads
Reinforcing the load-bearing wall is essential for adding significant weight. Consider:
- Adding Blocking: Install horizontal wood blocks between studs to increase the wall’s strength and provide extra anchor points for screws or brackets.
- Doubling Up the Studs: Doubling the studs in areas under high load improves load-bearing capacity. This technique is common for walls supporting heavy cabinets or gym racks in garages.
2. Use the Right Fasteners and Mounting Techniques
Mounting items correctly ensures that they stay secure over time. Do not attach objects directly to the drywall, as it can’t handle much weight. Instead,
- Find the Studs: Always use a stud finder to anchor into the studs, not the drywall.
- Use Anchors: For non-load-bearing walls, toggle bolts and metal anchors distribute weight more evenly, allowing you to mount light shelves or artwork.
3. Follow Building Codes and Best Practices
Compliance with building codes ensures your project is structurally sound.
- Consult Span Tables: Use span tables to determine how much weight a particular 2×4 configuration can hold based on stud spacing and load type.
- Inspect for Weak Points: Check for signs of moisture damage, bowing, or cracks in studs. These can weaken the wall and compromise its weight capacity over time.
4. Distribute the Weight Evenly
Even on a load-bearing wall, concentrated weight in one area can cause issues.
- Spread Out the Load: Install shelves or cabinets across multiple studs for even weight distribution.
Expert Tip: “For long, heavy shelves, use brackets at every stud to prevent sagging over time.”
Bonus Information
What Is the Pull-Out Strength of Screws in Wood?
The pull-out strength of a screw in a wood stud is the force that will be required to pull it out of the stud. It is also known as the allowable withdrawal load.
The allowable withdrawal load depends on the wood type, screw diameter, and screw penetration in the wood stud. The formula to calculate it is
F = 2850 X SG2 X D X P
where
F = allowable withdrawal load (lb)
SG = specific gravity of oven-dry wood
D = diameter of screw (in)
P = penetration of screw (in)
As an example, a #8, screw (diameter 5/32” or 0.164 in) penetrating 1” in Canadian Spruce (SG = 0.45) stud will have an allowable withdrawal load of around 95 pounds.
The allowable withdrawal load is, in fact, a critical parameter that will determine the load a 2X4 wall can hold. The actual load should be not over 50% of the allowable load.
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and useful.