Detached Garage Electrical Code: 5 Absolutely Important Sections!
garagemadesimple.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com . The website is also an affiliate of a few other brands.
Detached Garage Electrical Code: Why Do You Need to Know?
Now that your detached garage is almost ready you have to start thinking about electrification. Before you start, you must have at least a rudimentary knowledge of the Detached Garage Electrical Code.
Of course you need to run a cable from the main panel in the house to a subpanel in the detached garage. Then you need to do the wiring from the subpanel breakers to the lights, appliances & outlets.
The Detached Garage Electrical Code is the relevant sections of the NEC (National Electrical Code).
It is important to know the NEC code before doing any electrical work in a detached garage because garages are often used for a variety of purposes, including storing flammable liquids and gases, working with power tools, and charging electric vehicles.
These activities can pose a fire hazard if electrical wiring is not installed correctly.
Having basic knowledge of the Detached Garage Electrical Code, as laid out by NEC, before doing any electrical work in a detached garage, will ensure:
- Safety: The NEC code is designed to protect people and property from electrical hazards. It includes requirements for wiring methods, equipment, and safety devices. By following the NEC code, you can help to reduce the risk of fire, electrical shock, and other accidents.
- Compliance: Many municipalities require homeowners to obtain a permit and have their electrical work inspected before it is covered up. In order to pass inspection, your electrical work must comply with the NEC code.
- Insurance Claim Processing: If you have a fire or other electrical accident in your detached garage, your insurance company may deny your claim if your electrical work was not done to code.
Before you get into all of that you better get to know NEC, at least the very basics.
Detached Garage Electrical Code: Key Takeaways
| Topic | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Why do you need to know? | To ensure safety, compliance, and insurance claim processing. |
| What is NEC? | The National Electrical Code is the benchmark for safe electrical design, installation, and inspection. |
| What is the code for Branch Circuits? | Section 210.11(C)(4) requires at least one 120-volt, 20-ampere branch circuit shall be installed. |
| What is the code for Outlets? | Section 210.52(G)(1) requires at least one 20-amp outlet in each vehicle bay, located not higher than 5 ½ ft. All outlets must be GFCI protected. |
| What is the code for Receptacle Spacing? | Section 210.52(A)(1) requires that no point in the garage measured horizontally is more than 6 ft. from an receptacle outlet. |
| What is the code for GFCI? | Section 210.8 (A) requires that all 125-volt, single-phase, 15- and 20-ampere receptacles shall have GFCI protection for personnel.. |
What is the National Electrical Code (NEC)?
2023 National Electrical Code (NEC) is the latest version that covers everything electrical, including homes & garages. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) issues NEC and updates it every three years.
In their own words:
Adopted in all 50 states, NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC) is the benchmark for safe electrical design, installation, and inspection to protect people and property from electrical hazards.
NFPA 70
The NEC code is applicable to all the 50 states of the US, but different states may be at different stages in their adoption process. To find out at which stage your state is and therefore the version that is applicable to your state please check the link to NFPA – NEC Adoption Map.

What Is the Electrical Code for Outlets in a Garage?
An important section when it comes to detached garage electrical code is:
Section 210.11(C)(4) Garage Branch Circuits
Section 210.11(C)(4) Garage Branch Circuits is specific to outlets in a garage and states that:
In addition to the number of branch circuits required by other parts of this section, at least one 120-volt, 20-ampere branch circuit shall be installed to supply receptacle outlets required by 210.52(G)(1) for attached garages and in detached garages with electric power. This circuit shall have no other outlets.
Exception: This circuit shall be permitted to supply readily accessible outdoor receptacle outlets.
The important point to note here is that the above code uses the word “at least”. There is no mention of “at most”. So, while having just one outlet will make your garage code compliant, it is hardly a practical solution.
You certainly need many more outlets in your garage, located at a convenient distance from each other. The biggest advantage of having sufficient outlets, especially in a 2 or 3 car garage is that you can plug in vacuum cleaners, pressure washers, floor heaters or extra lights, without running long lines of extension cords.
Extension cords are not the safest electrical devices. People tripping over extension cords is not uncommon. Old frayed extension cords can also cause sparking and short circuiting.
Section 210.11(C)(4) Garage Branch Circuits refers to Section 210.52(G)(1) Garages. Hence, for the purpose of fully understanding detached garage electrical code you must consider:
Section 210.52(G)(1) Garages
Section 210.52(G)(1) Garages is specific to where the outlet must be placed and states that:
In each attached garage and in each detached garage with electric power, at least one receptacle outlet shall be installed in each vehicle bay and not more than 1.7 m (5 ½ ft) above the floor.
Exception: Garage spaces not attached to an individual dwelling unit of a multifamily dwelling shall not require a receptacle outlet in each vehicle bay.
Based on this section:
- An attached garage should have at least one outlet per parking bay which must be located not higher than 5 ½ ft.
- A detached garage should have at least one outlet (irrespective of the number of parking bays) which must be located not higher than 5 ½ ft.
How High Should an Outlet Be in a Garage?
The outlet(s) that are required to comply with Section 210.52(G)(1) Garages must not be higher than 5 ½ ft. However, there is no code for how low they can be. For practical reasons, namely convenience and to prevent floor water from reaching them, the ideal height is between 12” and 18”.
The other outlets in the garage that do not need to comply with Section 210.52(G)(1) Garages can be placed at any height that is convenient and will let the cord run as straight and short as possible.
Some recommended (not mandatory) heights are:
| Appliance / Utility | Height |
| Workshop Table or Bench | 34” – 38” |
| Table for Computers & Accessories | 28” – 30” |
| Household Appliances such as Refrigerators etc. | 48” |
| Garage with lot of DIY Activity (The height will let you place a drywall or plywood board against the wall without obstructing the outlet) | 50” |
| Garage Door Opener | On Garage Ceiling |
How Far Apart Should Outlets Be Spaced?
There is no specific provision for how far apart outlets should be in a garage. However, Section 210.52 Dwelling Unit Receptacle Outlets has regulations for habitable spaces of the home.
While a garage may not fall under the purview of habitable space, there is no harm in following the same guidelines as those for habitable spaces. The relevant Section is:
Section 210.52(A)(1) Spacing
Section 210.52(A)(1) Spacing states that
Receptacles shall be installed such that no point measured horizontally along the floor line of any wall space is more than 1.8 m (6 ft) from a receptacle outlet.
Do All Garage Outlets Need to Be GFCI?
Both the 2023 National Electric Code (NEC) and the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC) require that all receptacles in a garage must be GFCI.
Section 210.8 of 2023 NEC Ground-Fault Circuit-Interrupter Protection for Personnel
Section 210.8 of 2023 NEC Ground-Fault Circuit-Interrupter Protection for Personnel states that
Ground-fault circuit-interruption for personnel shall be provided as required in 210.8(A) through (F). The ground-fault circuit-interrupter shall be installed in a readily accessible location.
The following subsection is important as it clarifies further.
Section 210.8 (A) Dwelling Units
Section 210.8 (A) Dwelling Units states
All 125-volt, single-phase, 15- and 20-ampere receptacles installed in the locations specified in 210.8(A)(1) through (11) shall have ground-fault circuit-interrupter protection for personnel.
Garage is listed as one of the locations in Sections 210.8(A)(1) through (11) and as such the detached garage electrical code requires all outlets in a detached garage to be GFCI protected.
For more details on detached garage electrical code related to GFCI requirements, do check out the following earlier posts:
- Why Is GFCI Required In Garage? (A Simple Way To Stay Safe!)
- Do Garage Lights Need to Be GFCI Protected? (Enlightening Facts!)
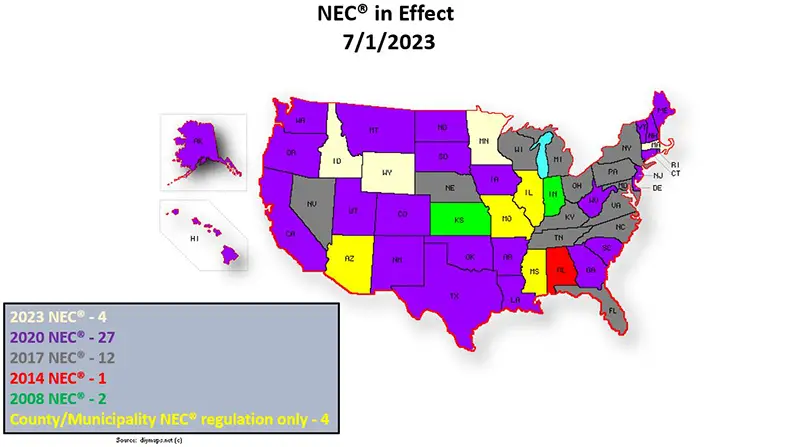
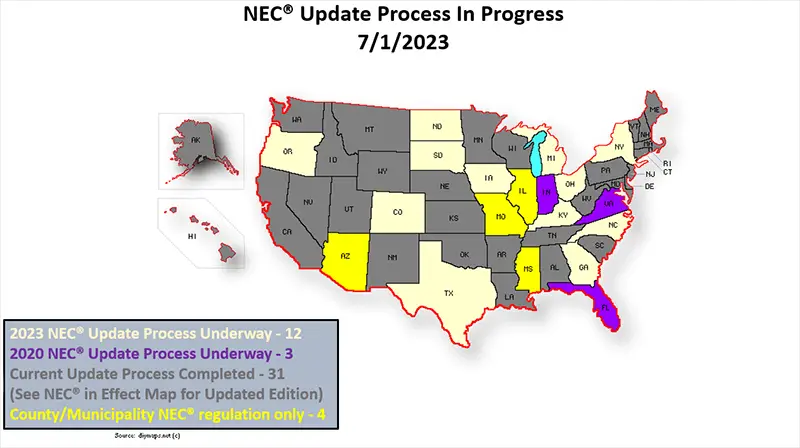
Statewide Status of NEC Code Enforcement as of July 1, 2023
Below are 2 maps that give the statewide status of NEC Code Enforcement as of July 1, 2023 (Data Source : NEC Adoption & Use)
DISCLAIMER: What Is the Safest Way to Handle Electrical Wires?
This post is for information only. I strongly recommend that all electrical work should be entrusted to licensed professional electricians. In case you do decide to do some of the work yourself, make sure that:
“Treat all electrical wiring, even “de-energized” ones as if it is live, unless it has been locked out and tagged”
You must follow the basic safety guidelines, as under:
- Use protective eyewear, especially when drilling or grinding metal
- Wear insulated rubber gloves when working on any circuit or branch circuit
- Always use insulated tools while working with electricity
- De-energize the electrical wires on which you will be working. Tag the circuit breaker to prevent someone from switching it on accidently
- Electrical wiring in wet or damp locations or underground must be within a PVC conduit
- Underground wiring conduits should be at least 18 inches below grade as per code
- All receptacles for equipment that could be in wet or damp locations should be equipped with Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
- Never use old frayed cables, damaged insulation or broken plugs
- High voltage equipment should be properly grounded to insure electricity flows directly to the ground and not through the person in contact with the live wire
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and useful.