Sill Plate Anchor Bolt Requirements: An Updated Comprehensive Guide [2024]
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
1. What are Sill Plate Anchor Bolt Requirements?
Sill plate anchor bolt requirements are crucial for securing a building’s stability, especially in structures like detached garages or sheds.
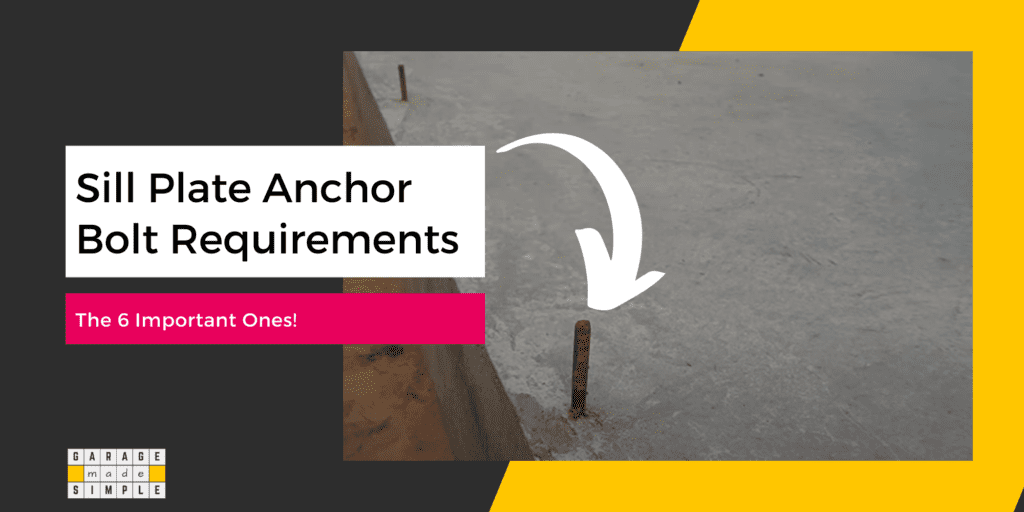
The sill plate anchor bolt secures the sill plate to the concrete foundation, providing structural stability and preventing lateral movement.
Key Requirements from the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC)
According to Section R403.1.6 of the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC), the following guidelines apply:
- Spacing: Anchor bolts should be spaced no more than 6 feet apart.
- Minimum Bolts: Each sill plate section must have at least two bolts, with one bolt no more than 12 inches from each end.
Example:
- An 8-foot long 2×4 sill plate requires at least two anchor bolts, placed 1 foot from each end.
- A 24-foot long garage wall, consisting of three 8-foot 2×4 sill plates, needs at least six anchor bolts.
While these requirements meet the IRC code, they may not always be sufficient for securing a garage wall to a concrete slab-on-grade. Local building codes might demand more anchor bolts based on factors like foundation design and expected lateral loads from wind speeds.
Best Practices for Anchor Bolt Placement
The best practices for anchor bolt placement, for enhanced stability, are:
- Bolt Placement: Use an anchor bolt centered in every alternate stud cavity.
- Stud Spacing: With a standard 16-inch on-center stud spacing, a 24-foot wall will have 18 stud cavities and should ideally have 9 anchor bolts.
- End Studs: Ensure each of the two end stud cavities has an anchor bolt, positioned in the center.
Final Recommendations
Always consult your local building code and a qualified structural engineer to determine the specific sill plate anchor bolt requirements for your project. This ensures compliance with regulations and enhances the safety and stability of your structure.
2. What Is the Code for Anchor Bolts on a Sill Plate?
The code for anchor bolts on a sill plate is designed to ensure that the structural integrity of a building is maintained by securely attaching the sill plate to the foundation. The International Residential Code (IRC) provides specific requirements to achieve this.
IRC Specifications
Section R403.1.6 of the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC), specifies the following key points for anchor bolts used on sill plates:
- Bolt Diameter: Anchor bolts must be at least 1/2 inch in diameter to provide sufficient strength and stability.
- Bolt Spacing: Anchor bolts must be spaced not greater than 6′ on center (OC).
- Bolt Depth: Bolts shall extend not less than 7″ into concrete.
- Bolt Location: Bolts shall be located in the middle third of the plate width.
- Bolt Numbers: Each sill plate section must have at least two bolts, with one bolt no more than 12 inches from each end.
- Material and Installation: The bolts should be made of corrosion-resistant materials and installed with washers for added security.
Understanding Local Amendments
While the IRC provides a comprehensive framework, local building codes may impose additional requirements based on regional factors such as weather patterns, seismic activity, or soil conditions. For example:
- Stricter Requirements: Some areas might require larger bolt diameters or closer spacing to withstand higher wind loads or seismic forces.
- Specific Materials: Certain jurisdictions may mandate the use of specific materials to combat local environmental conditions, like high humidity or salt air.
3. What Is the Purpose of Sill Plate Anchor Bolts?
The main purpose of sill plate anchor bolts is to resist lateral forces exerted on the garage superstructure by wind, earthquakes, etc.
Without sill plate anchor bolts the garage can shift or rotate. Anchor bolts, true to their name, help keep the garage securely anchored to the foundation, which is usually concrete slab-on-grade.
Key Purpose in Summary
- Structural Stability: Anchor bolts help keep the garage or structure securely anchored to its concrete foundation, usually a slab-on-grade.
- Lateral Force Resistance: They provide essential resistance against lateral forces, safeguarding the building during extreme weather events or seismic activity.
Types of Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts come in various forms, including bent or straight types, and are commonly known as J-bolts, L-bolts, or hold-down bolts.
Installation Methods
- Embedded in Wet Concrete: Sill plate anchor bolts are typically embedded into the concrete foundation while it is still wet. As the concrete cures, the bolts become a permanent part of the foundation.
- Post-Installation: Alternatively, holes can be drilled into the cured concrete foundation, and the anchor bolts are inserted and secured.
Securing the Structure
The sill plate connects the garage wall frame to the concrete foundation using anchor bolts, washers, and nuts. This secure connection is vital for the safety and stability of the structure.
Importance of Proper Installation
Proper installation of sill plate anchor bolts is critical to the building process. Building codes specify the type, size, spacing, and placement of anchor bolts to ensure that structures are safe and secure.
By adhering to these codes and guidelines, builders can ensure the long-term stability and safety of the construction.
4. How Are Sill Plates Attached?
The sill plates must be attached correctly to the slab-on-grade concrete foundation of the garage. Here is how to do it.
Steps for Attaching Sill Plates
- Preparation of the Foundation: Ensure the concrete foundation is level and free of debris. This provides a clean surface for the sill plate to rest on.
- Positioning the Sill Plate: Lay the sill plate along the perimeter of the foundation. Use treated lumber for the sill plate to prevent moisture damage.
- Drilling for Anchor Bolts: If not using pre-installed bolts, drill holes in the sill plate to match the location of the anchor bolts. The holes should be slightly larger than the bolt diameter to allow for adjustments.
- Installing Anchor Bolts: Insert the anchor bolts into the holes, making sure they are properly aligned with the pre-drilled holes in the sill plate. Use a washer and nut to secure each bolt tightly.
- Sealing the Plate: Apply a sill seal or foam gasket between the sill plate and the foundation to create a barrier against moisture and air infiltration.
- Securing with Fasteners: Use construction adhesive and galvanized nails or screws to fasten the sill plate to the foundation. This helps prevent movement and adds additional stability.
Ensuring Proper Attachment
- Check Alignment: Ensure the sill plate is straight and level before securing it to the foundation.
- Follow Local Building Codes: Adhere to local building codes for specifications on bolt placement, spacing, and materials.
5. What are the Different Types of Anchor Bolts?
Anchor bolts are designed to attach structural elements, such as sill plates to concrete. They are typically used to attach wood or steel frames to concrete, with one end embedded in the concrete and the opposite end threaded to the frame.
The Four Main Types of Anchor Bolts
- L-Shaped Anchor Bolts (J Bolts):
- Description: Named for their L or J shape, these bolts are typically cast-in-place, meaning they are set into the concrete as it is poured.
- Use: Once the concrete cures, the bolts are permanently secured, making them ideal for connecting wood or metal frames to foundations.
- Double End Rods with Plate:
- Description: These anchors have a plate washer on one end and are threaded on both ends.
- Use: Primarily used in constructing structural columns, highway signs, and other applications requiring strong support.
- Headed Anchor Bolts:
- Description: These bolts have a forged head on the unthreaded end.
- Use: Commonly used to secure structural columns, bridge railings, and light poles due to their robust anchoring capability.
- Swedge Bolts:
- Description: These bolts have a swedged end with multiple indentations that allow concrete to flow into them during installation.
- Use: Ideal for connecting girders and piers, providing a strong and stable connection.
6. Where Do Anchor Bolts Go on a Sill Plate?
The IRC Code and structural design principles dictate the correct positioning of anchor bolts. Here is the recommended placement guideline:
- Edge Distance: Anchor bolts should be positioned no more than 12 inches from the end of each sill plate section.
- Spacing Along the Plate: The bolts should be evenly spaced along the length of the sill plate, with a maximum distance of 6 feet between them.
- Center Alignment: For optimal stability, anchor bolts should be placed in the center of the sill plate’s width.
- Consideration of Stud Locations: When positioning anchor bolts, consider the location of wall studs. Ideally, bolts should be placed in alignment with alternate stud cavities.
7. How Deep Should Sill Plate Anchor Bolts Be in Concrete?
Section R403.1.6 of the 2021 IRC Code requires that sill plate anchor bolts shall be embedded a minimum of 7” into the concrete for residential construction.
The code considers this depth to be sufficient enough for the anchor bolt to resist lateral forces exerted on the garage by wind, earthquakes, etc.
Of course, the sill plate anchor bolt requirements by IRC, for the depth of the bolt is only the minimum stipulated.
The actual depth requirement would depend on the local building code and the calculations made by a qualified structural engineer for a specific project. The factors that a qualified structural engineer will take into account can be quite complex.
DEWALT XTREME 12V MAX* Cordless Drill / Driver Kit, 3/8-Inch
DEWALT XTREME 12V MAX* Cordless Drill
This cordless drill is compact and performance packed, ideal for precision applications like drilling small pilot holes. It accepts up to a 12-inch spade bit.
At only 5.97-inch length, it is packed to perform with a 2-speed transmission. It also features a bright LED positioned light on the foot to illuminate work areas.
8. What Size Sill Plate Anchor Bolts Do I Need?
The same section, namely Section R403.1.6 of the 2021 IRC Code requires that sill plate anchor bolts shall be a minimum of ½” in diameter.
This requirement is, of course, the bare minimum. A sill plate anchor bolt that is less than ½” in diameter would likely just snap under any kind of lateral load.
However, the actual size of sill plate anchor bolts will probably need to be larger. The size would depend on various factors, such as the foundation load-bearing capacity, the design of the structure, etc.
A detached garage is a relatively simple structure and you should be fine if you comply with the local building authority’s sill plate anchor bolt requirements.
For a more complex building such as your home, you should entrust the entire design (including everything to do with sill plate anchor bolt requirements) to a professional structural design firm.
They can run load calculations based on all kinds of relevant factors such as wind speeds in the area, etc.
9. What Is the Minimum Anchor Bolt Spacing for a Sill Plate?
The minimum anchor bolt spacing for a sill plate is 6 feet, as specified by the International Residential Code (IRC).
However, local building codes may impose stricter requirements based on regional factors such as wind or seismic activity. You always need to adhere to the local building codes.
10. What Are Anchor Bolts Made Of? Is Corrosion a Concern?
Anchor bolts can corrode over time due to exposure to moisture and other environmental factors. Corrosion can weaken the anchor bolts and defeat their basic purpose.
To prevent corrosion, anchor bolts should be made of a corrosion-resistant material, such as stainless steel or hot-dip galvanized steel.
Stainless steel anchor bolts are resistant to corrosion and are often used in marine or coastal environments where saltwater corrosion is a concern. Hot-dip galvanized steel anchor bolts are coated with a layer of zinc that protects the steel from corrosion.
As pressure-treated wood is recommended for sill plates in a garage, hot-dipped galvanized steel anchor bolts are a better option. The copper-based chemicals in the pressure-treated sill plates will not be able to corrode them.
11. When Should Sill Plate Anchor Bolts Be Placed in Concrete?
Sill plate anchor bolts can be placed in a concrete slab-on-grade using one of the following techniques.
Cast In Place Anchor Bolts
“Cast in place” anchor bolts are a common practice. Anchor bolts are installed in the wet concrete before it hardens so that they become a permanent part of the slab-on-grade foundation.
“Cast in place” anchor bolts are the most secure option as a very strong bond develops between the anchor bolts and the concrete slab.
The location, spacing, and depth of the anchor bolts must be marked before placing anchor bolts to ensure there are no errors and all sill plate anchor bolt requirements are complied with.
Post Installed Anchor Bolts
Post-installed anchor bolts require the drilling of holes into the hardened concrete slab after it has cured. Anchor bolts are then hammered into the holes.
It is important to keep the hole diameter just a little bit smaller than the anchor bolt diameter to get a tight fit.
This method is typically used when anchor bolts were not placed in the slab at the time of the pour, or when additional anchor bolts are needed.
Epoxy Anchored Anchor Bolts
In the epoxy-anchored method, holes are drilled into the concrete slab and filled with epoxy. The anchor bolts are inserted into the epoxy-filled holes before the epoxy begins to set. Naturally in this method, the hole diameter should be larger than the anchor bolt diameter.
This method is preferred where extra strength and stability are needed, such as in seismically active areas.
Mechanical Anchoring
Mechanical anchoring involves using a special tool to install an anchor into a pre-drilled hole in the concrete. This is a fast and easy method but it’s limited by the size of the anchor and the strength of the concrete.
Thank you very much for reading the post. I do hope you found it informative and useful.